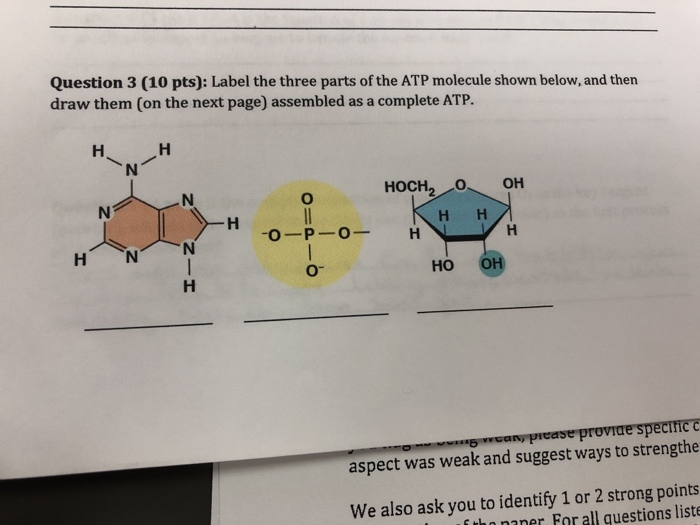
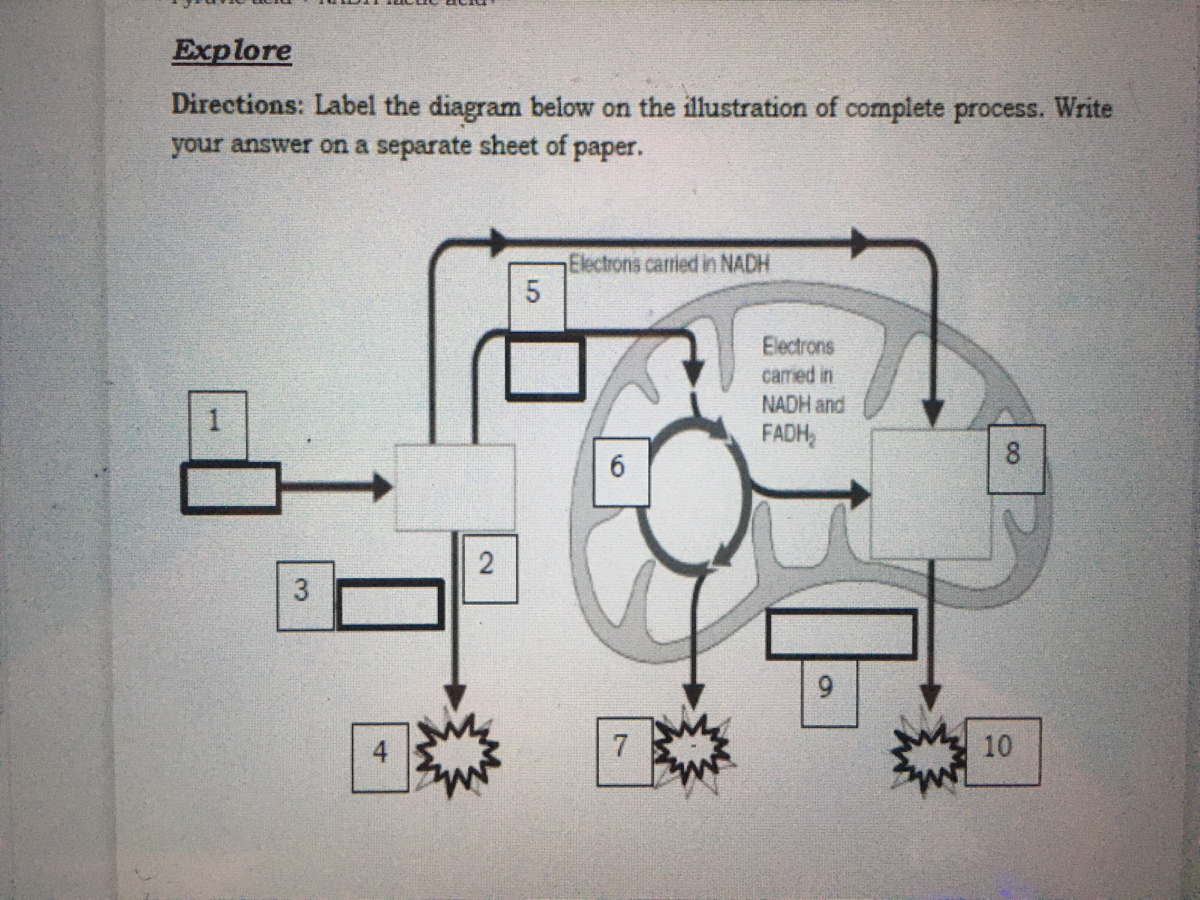
41 label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below
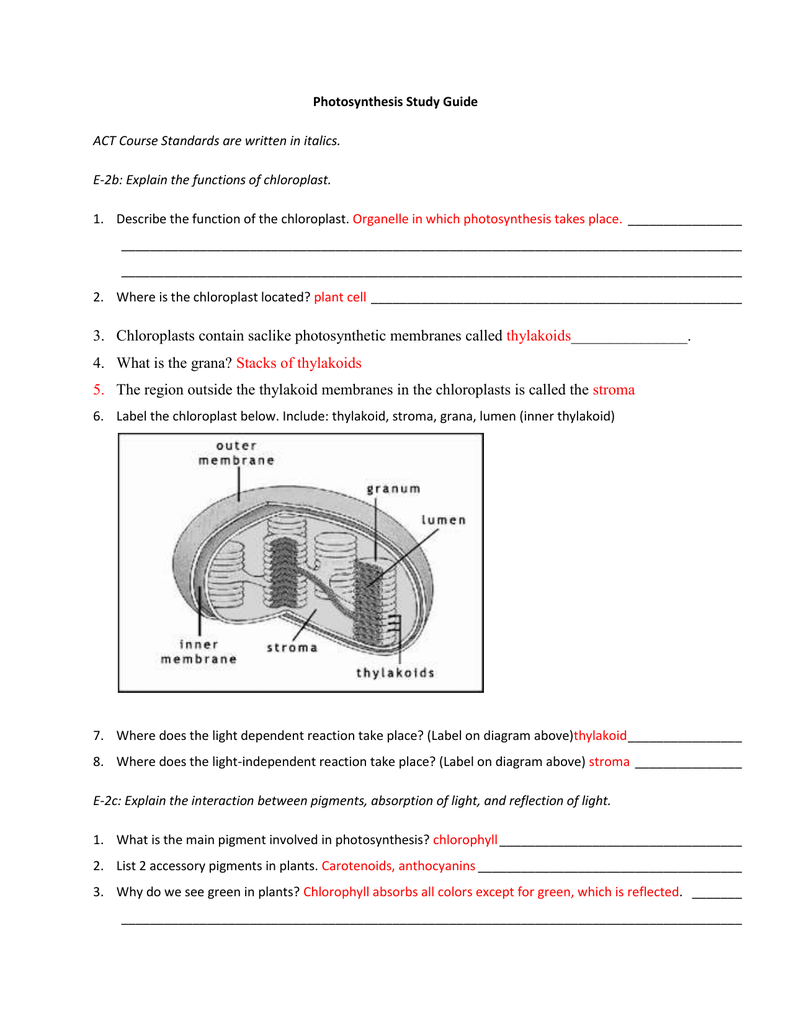
DOC Bio07_TR_U03_CH08.QXD - Pearson Education 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. 63 Name Class Date 7. When is the energy stored in ATP released? 8. PDF Chapter 3 Review Materials Key - wtps.org 3. Using the following terms, correctly label all cell parts indicated by leader lines in Figure 3.6. Then select different colors for each structure and use them to color the coding circles and the corresponding structures in the illustration. 61 Nuclear membrane Golgi apparatus Plasma membrane Mitochondrion Chromatin threads Nucleolus
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function This is a structural diagram of ATP. It is made up of the molecule adenosine (which itself is made up of adenine and a ribose sugar) and three phosphate groups. It is soluble in water and has a high energy content due to having two phosphoanhydride bonds connecting the three phosphate groups. Functions of ATP Energy Source

Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below
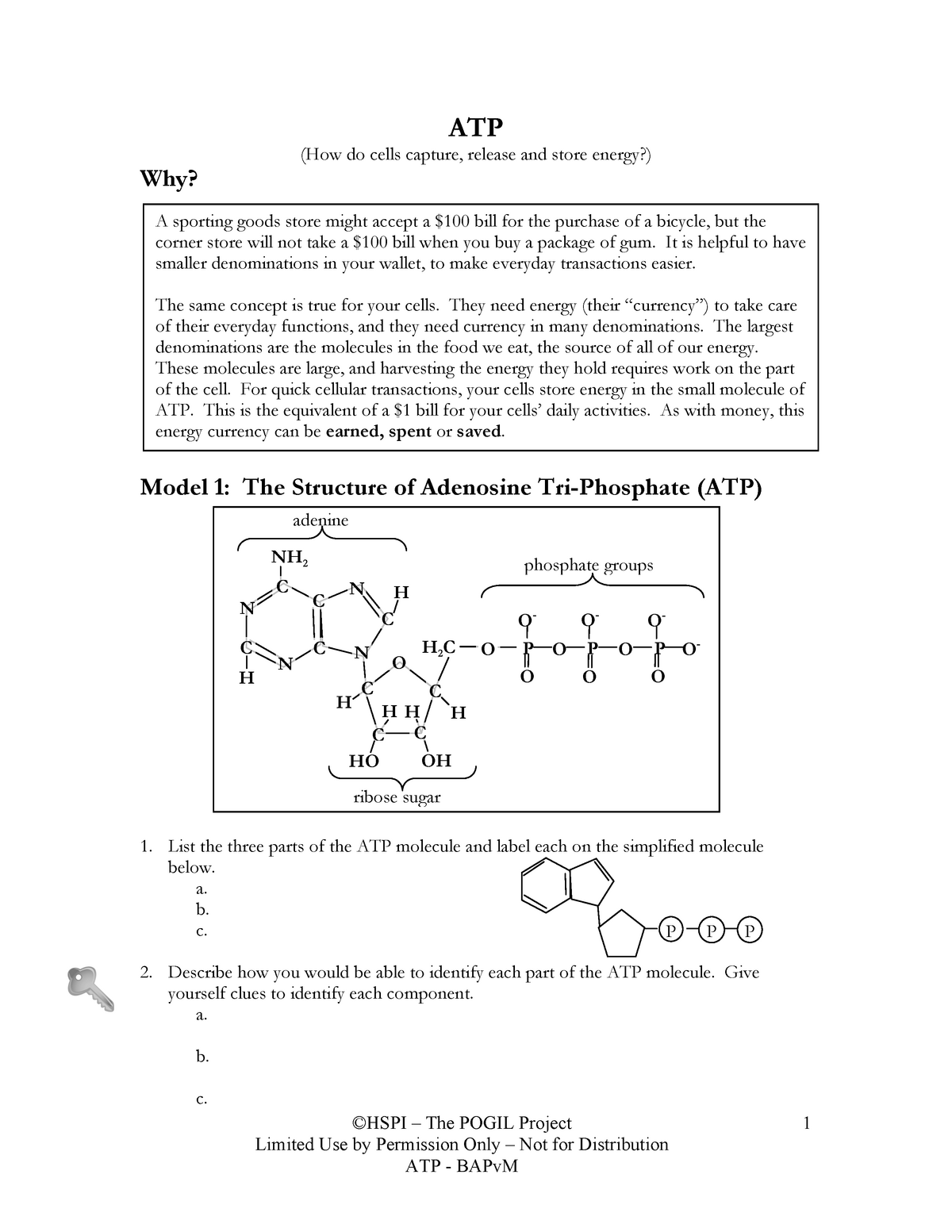
Module One- Human Body & Chemistry of Life Flashcards - Quizlet Complete each statement below regarding the body's structural hierarchy, then arrange them in order (top to bottom) from smallest to largest. -Collections of like cells performing a similar function are called tissues. They are divided into four major categories: connective, nervous, epithelial, and muscular. PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) - Mystr Nakashima Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P TYPES OF ORGANISMS Chemical Energy and ATP(page 202) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. PDF ATP - Loudoun County Public Schools ATP (How do cells capture, release and store energy?) Why? Model 1: The Structure of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) 1. List the three parts of the ATP molecule and label each on the simplified molecule below. a. b. c. 2. Describe how you would be able to identify each part of the ATP molecule. Give yourself clues to identify each component. a. b. c.
Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. Caveat fluorophore: an insiders’ guide to small-molecule ... Dec 23, 2021 · Common small-molecule and protein-based fluorophores categorized by excitation window; spectral properties are listed below each molecule as λ abs (nm) ε (M −1 cm −1) λ em (nm) Φ f and the ... What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture: ATP AND BIOLOGICAL ENERGY - Estrella Mountain Community College This covalent bond is known as a pyrophosphate bond. We can write the chemical reaction for the formation of ATP as: a) in chemicalese: ADP + Pi + energy ----> ATP. b) in English: Adenosine diphosphate + inorganic Phosphate + energy produces Adenosine Triphosphate. The chemical formula for the expenditure/release of ATP energy can be written as ... DOC Bio07_TR_U03_CH08.QXD What are two ways in which cells use the energy provided by ATP? a. b. Using Biochemical Energy (pages 202-203) 10. Why is it efficient for cells to keep only a small supply of ATP on hand? 11. Circle the letter of where cells get the energy to regenerate ATP. a. ADP. b. phosphates. c. foods like glucose. d. organelles
ATP BIS 2C.pdf - CONSERVATION OF ENERGY IN ATP By the end... - Course Hero ATP is a nucleotide composed of three general parts: a nitrogenous base, a sugar and three phosphate groups. a. Label the three parts of the nucleotide below. b. Draw an arrow to the two phosphoanhydride bonds in the ATP molecule. c. Write a balanced equation for the hydrolysis of one of the phosphoanhydride bonds in the ATP, indicate all ... PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) - Biology || Miss B Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? ... Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about the light-dependent reactions. a. ... ATP synthase allows H+ to pass through the protein, causing the protein to rotate. As it rotates, it ATP-Student - ATP - ©HSPI - The POGIL Project Limited Use by Permission ... ATP (How do cells capture, release and store energy?) Why? Model 1: The Structure of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) List the three parts of the ATP molecule and label each on the simplified molecule below. a. b. c. Describe how you would be able to identify each part of the ATP molecule. Give yourself clues to identify each component. a. b. c. PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, SE - Loudoun County Public Schools Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? 7. When is the energy stored in ATP released? TYPES OF ORGANISMS © Pearson Education, Inc.
Fatty acid - Wikipedia Alternatively, the label "ω−x" is written "n−x", where the "n" is meant to represent the number of carbons in the chain. In either numbering scheme, the position of a double bond in a fatty acid chain is always specified by giving the label of the carbon closest to the carboxyl end. PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP 4. How is ATP different from ADP? ATP has three phosphate groups, whereas ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples ATP POGIL.docx - ATP (How do cells capture, release, and... Model 1: The Structure of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) 1. List the three parts of the ATP molecule and label each on the simplified molecule below. a. _____ b. _____ c. _____ 2. Describe how you would be able to identify each part of the ATP molecule. Give yourself clues to identify each component. PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, TE - Scarsdale Public Schools Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that living things use to store energy? Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP 4. How is ATP different from ADP? ATP has three phosphate groups, while ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples
CH103 – Chapter 8: Homeostasis and Cellular Function – Chemistry b) HF is a weak acid even though F is strongly electronegative. This is because the H-F molecule can form strong hydrogen bonds with the water molecules and remain in a covalent bond that is harder to dissociate. Thus, beaker #2 is also a good choice for this molecule, as only some of the H-F will dissociate to H3O+ and F- ions.
DOC 013368718X_CH08_115-128.indd - tesd.net of ATP are the key to its ability to store and supply energy. ATP releases energy when it breaks bonds between its phosphate groups. Most cells only store enough ATP for a few seconds of activity. Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions 8-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery.
ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy ATP structure, ATP hydrolysis to ADP, and reaction coupling. ATP structure, ATP hydrolysis to ADP, and reaction coupling. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
PDF TYPES OF ORGANISMS Type Description Examples What are two ways in which cells use the energy provided by ATP? a. b. Using Biochemical Energy (pages 202-203) 10. Why is it efficient for cells to keep only a small supply of ATP on hand? 11. Circle the letter of where cells get the energy to regenerate ATP. a. ADP b. phosphates c. foods like glucose d. organelles
PDF Scarsdale Public Schools / Overview ATP has three Phosphate groups, while ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups p p 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? It can add a phosphate group to ADP molecules, producing ATP molecules. 7.
SOLVED:VISUAL SKILLS This computer model shows the four parts of ATP ... VISUAL SKILLS This computer model shows the four parts of ATP synthase, each part consisting of a number of polypeptidelsubunits (the structure in gray is still an area of active research. Using Figure 9.14 as a guide, label the rotor, stator, internal rod, and catalytic knob of this molecular motor.
PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P TYPES OF ORGANISMS Chemical Energy and ATP(page 202) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6.
A&p test 2 Flashcards | Quizlet -6CO2, 6H2O, 32 ATP -Pyruvic acid, lactic acid, 2 ATP -Pyruvic acid, 4 ATP -6CO2, 6H2O, 2 ATP 6CO2,6H20,32 ATP Exocrine glands can be further classified into------ glands, which are composed of a single epithelial cell, and----- glands, that are composed of many cells. unicellular, multicellular Extracellular matrix consist of lacunae and lamellae
A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 1 ... May 16, 2022 · Like ATP, NO acts as a biological signaling molecule. This dissolved gas rapidly diffuses across cell membranes and regulates various functions across the body . The vascular endothelium is the ...
2017-2018 - Science with Mrs. Floria - Google Below is the structural Formula for ATP (from Wikipedia). Notice the three phosphate molecules on the left. ... Be able to label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. ... You must label the lungs, oral cavity, nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, and diaphragm. (You may use the diagram below for help)
Quantitative Chemical Proteomics Reveals New Potential Drug ... Sep 28, 2011 · It allows the purification and identification of several hundred kinases and other ATP-binding proteins from cell lines or tissues (22, 23). The second element is intensity-based label-free quantitative mass spectrometry that enables the identification and relative quantification of the purified proteins across many biological samples ( 24 ).
Protein Digestion and Absorption – Nutrition: Science and ... The mashed egg pieces enter the stomach from the esophagus. As illustrated in the image below, both mechanical and chemical digestion take place in the stomach. The stomach releases gastric juices containing hydrochloric acid and the enzyme, pepsin, which initiate the chemical digestion of protein. Muscular contractions, called peristalsis ...
atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. In the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe the FANCM-family DNA helicase FmI1 directs NCO recombination formation during meiosis. u Based on these helicase motifs, a number of helicase superfamilies have been distinguished. In: Spies, M.
PDF Science With Mr. Haug Chemical Energy and ATP (pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. P P p 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy?
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule | Chegg.com Transcribed image text: Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions &-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low battery? What arc two ways in which the diagram shows an increase in energy? Describe the concepts shown in the diagram.
Biochemistry PDF | PDF | Cell (Biology) | Biochemistry - Scribd Each reaction is designed to produce some hydrogen ions that can then be used to make energy packets (ATP). In prokaryotes, glycolysis is the only method used for converting energy. The second pathway, called the Krebs cycle, or citric acid cycle, occurs inside the mitochondria and can generate enough ATP to run all the cell functions.
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams Cellular Respiration Equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 38*ATP. 10. Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, " biological machines " also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work. Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the ...
PDF ATP - Loudoun County Public Schools ATP (How do cells capture, release and store energy?) Why? Model 1: The Structure of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) 1. List the three parts of the ATP molecule and label each on the simplified molecule below. a. b. c. 2. Describe how you would be able to identify each part of the ATP molecule. Give yourself clues to identify each component. a. b. c.
PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) - Mystr Nakashima Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P TYPES OF ORGANISMS Chemical Energy and ATP(page 202) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6.
Module One- Human Body & Chemistry of Life Flashcards - Quizlet Complete each statement below regarding the body's structural hierarchy, then arrange them in order (top to bottom) from smallest to largest. -Collections of like cells performing a similar function are called tissues. They are divided into four major categories: connective, nervous, epithelial, and muscular.
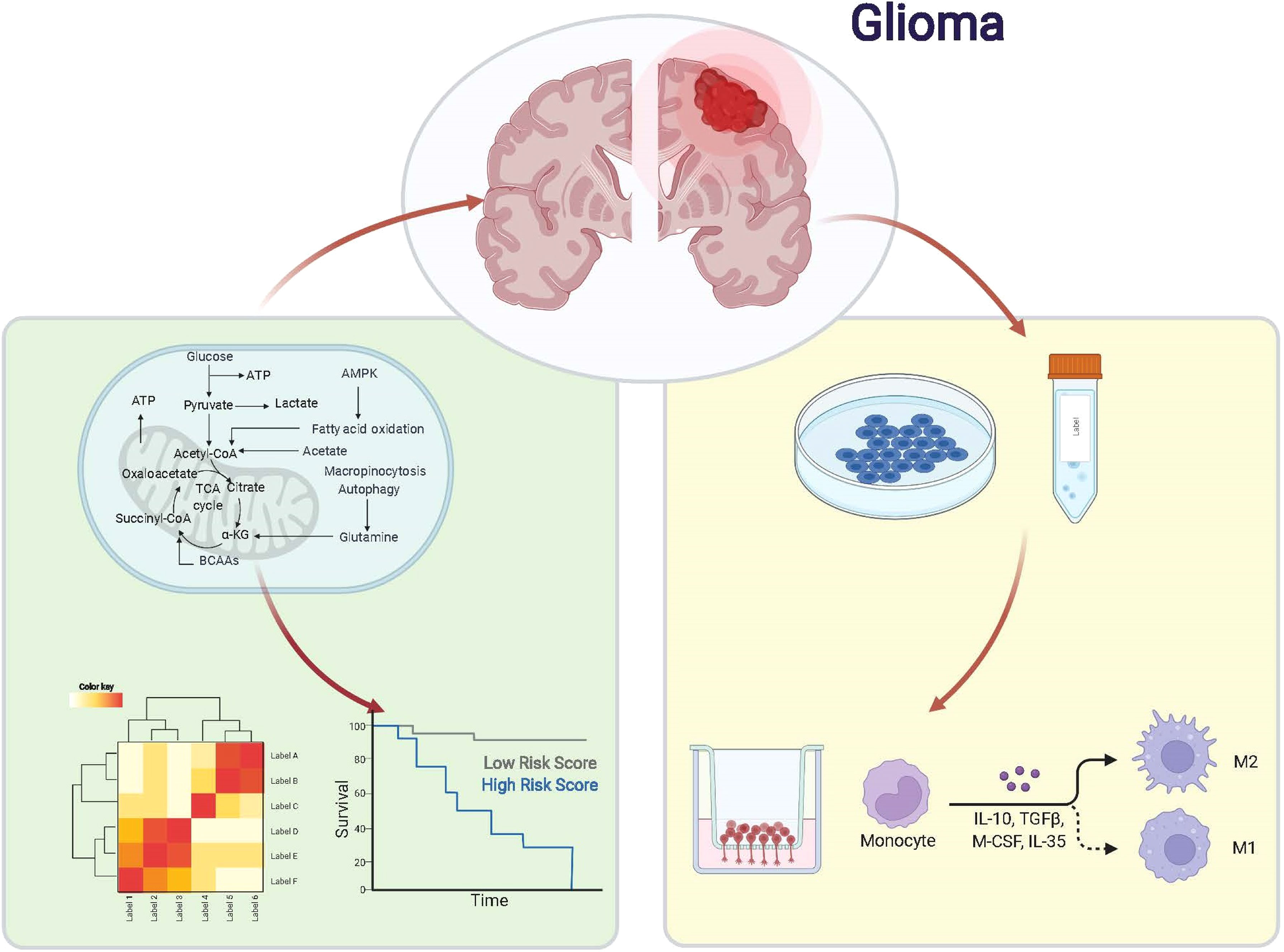






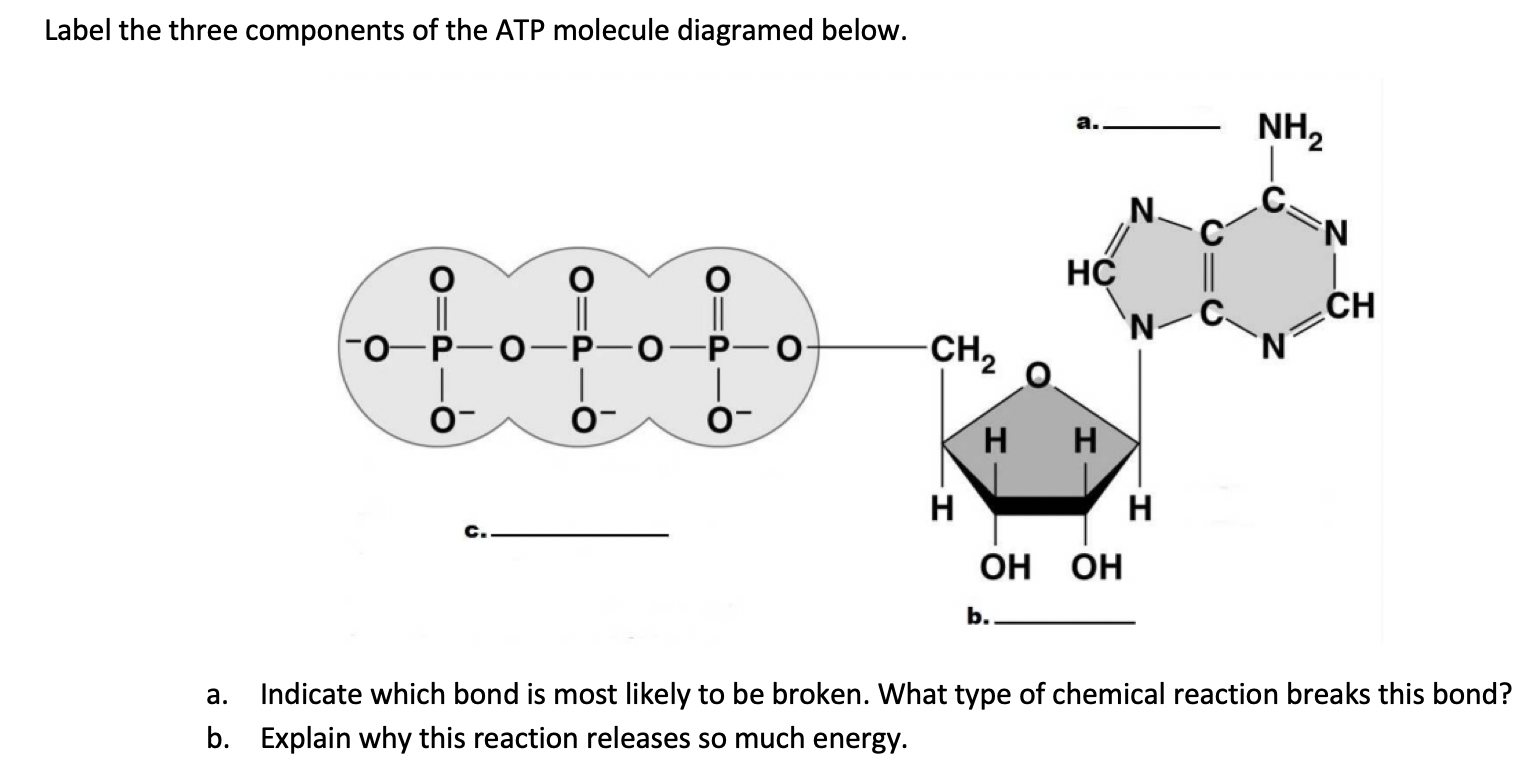













Komentar
Posting Komentar